Malaysia
Malaysia: The pension system in 2016
Private sector employees and non-pensionable public sector employees contribute to the provident fund, with social assistance paid to those with insufficient income.
Qualifying conditions
Funds can be withdrawn from age 55, and retirement is not necessary. Eligibility to social benefits, however, is from age 60.
Benefit calculation
Defined contribution
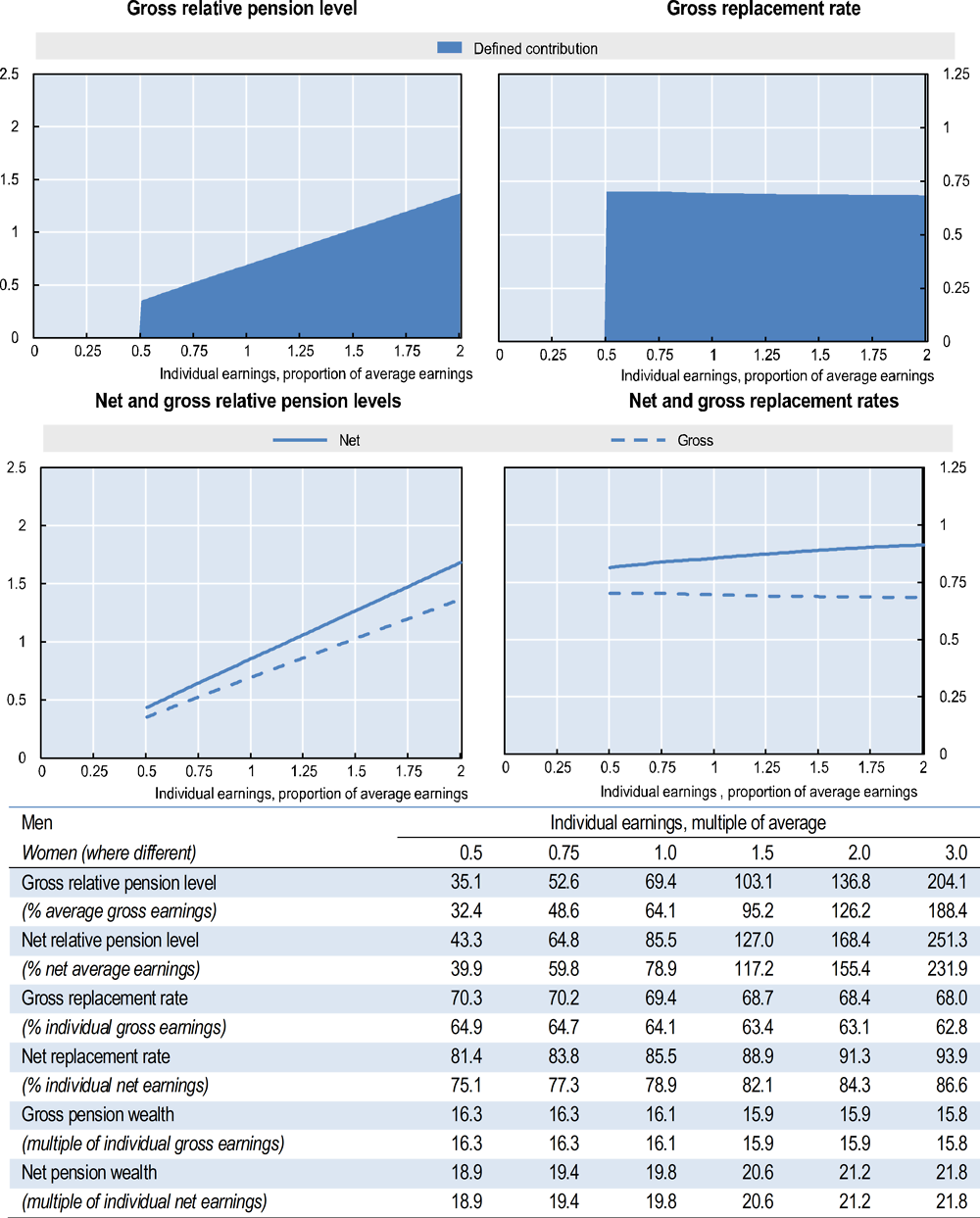
Employees pay 8% of monthly earnings to the provident fund according to wage classes, when aged up to age 60, and 4% between age 60 and 75. Employers pay 13% of monthly earnings according to wage classes for employees up to 60 years of age and earning under RM 5 000 per month, and 12% for earnings above RM 5 000 per month. Employer contributions are 6.5% and 6% respectively, between ages 60 and 75, for those earning under and above RM 5 000 per month. Minimum monthly earnings for the contribution are MYR 10 and there is no ceiling for the contribution. Insured persons can make voluntary additional contributions.
The contribution is made to two different accounts: 70% of contribution to Account 1 and 30% to Account 2. It is possible to receive pension in a lump sum, monthly instalments or a combination of both. The minimum total amount to be paid in monthly instalments is RM 250 with the minimum period being 12 months, with a minimum withdrawal at any time of at least MYR 2 000, or a combination of these options. For comparison with other economies, for replacement rate purposes the pension is shown as a price-indexed annuity based on sex-specific mortality rates.
The guaranteed minimum interest rate is 2.5% a year. If funds remain in the accounts after age 55, fund members continue to earn compound interest until age 100.
Old-age assistance
A monthly benefit of RM 300 is paid to those aged 60 and assessed as needy (below poverty line), with no financial support from other family members.
Variant careers
Early retirement
It is possible to make a one-time withdrawal of savings at age 50 from Account 2.
Late retirement
It is possible to defer retirement and continue to make contributions after normal pension age.
Personal income tax and social security contributions
Taxation of workers
The mandatory and voluntary provident fund contributions up to RM 6 000 a month are tax deductible. Employees below age 55 earning RM 3 000 or less a month and casual workers need to be covered by social insurance. The insurance does not cover old-age pension, but disability, survivor and other pensions and grants. The contribution rate is 0.5% of monthly earnings for employees and 1.75%.
Taxation of worker’s income
Social security contributions payable by workers
Workers make contributions as described above.
Taxation of pensioners
There is no additional tax relief for pensioners.
Taxation of pension income
Pension income is tax exempted.
Social security contributions payable by pensioners
Pensioners do not pay any social security contributions.