1. From the Great Lockdown to the Great Divergence
This chapter examines the contrasting impact on the global economy of the COVID-19 pandemic, Russia’s war of aggression against Ukraine and other recent crises. While rich countries are beginning to turn the corner on the COVID-19 crisis, prospects of a strong and sustainable recovery in developing countries are vanishing – signs of an emerging two-track recovery that is widening inequalities between and within countries.
1.1.1. A fragile “K-shaped” recovery is accentuating economic and financial disparities across countries in the wake of successive crises
The pandemic triggered a global recession of a magnitude not seen since the Second World War. As described in the previous edition of the Global Outlook on Financing for Sustainable Development (hereinafter Global Outlook), the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic at the beginning of 2020 sent massive shockwaves through the global economy (OECD, 2020[1]). The quick propagation of the pandemic caught many countries off guard. As numerous countries locked down their populations in an effort to control the spread of the disease, a large part of the global economy came to a halt – a period now referred to as the Great Lockdown. By its nature, the COVID-19 crisis has had a complex and profound impact on the global economy and financial system. In contrast to previous crises that were triggered by either a demand shock (the 2008-09 global financial crisis) or a supply shock (the Hokkaido earthquake and tsunami), the Great Lockdown generated a simultaneous demand and supply shock by pushing a large share of the world’s population into inactivity. The result was a massive contraction of the global economy, with world gross domestic product (GDP) growth falling by -3.4% in 2020 (OECD, 2021[2]).
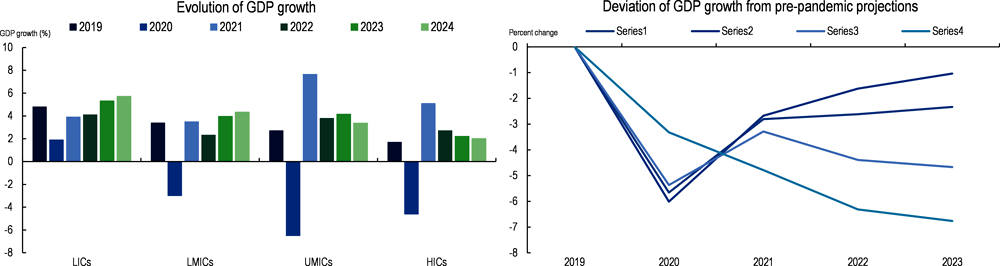
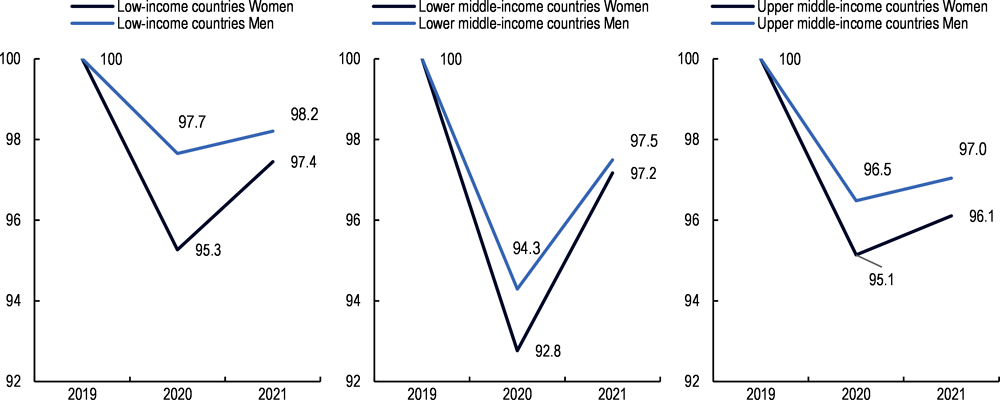
The gradual reopening of countries in the second half of 2020 was the prelude to a swift but fragile global recovery. As government restrictions started to ease and businesses reopened, global economic activity picked up pace towards the end of 2020: world GDP was down by -10% between Q4 2019 and Q2 2020 but rebounded by 8% between Q2 and Q4 2020 (OECD, 2021[2]). Shortly afterwards, the progressive reopening of borders prompted a recovery of world trade, which increased by +9.3% in 2021 after a -8.2% slump the previous year (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 2022[3]). This recovery, combined with the entry into action of the stimulus packages launched by some major economies, contributed to shoring up world GDP by +5.6% in 2021. However, the incipient global recovery hid large disparities between countries at different levels of development. While high-income countries (HICs) and upper middle-income countries (UMICs) registered a larger drop in economic output in 2020, most of these countries were already experiencing a strong recovery by 2021, with economic growth exceeding pre-crisis levels due in part to a rebound effect. Low-income countries (LICs) and lower middle-income countries (LMICs) experienced a softer recession in 2020 but are now facing a weaker recovery (Figure 1.1, left side).
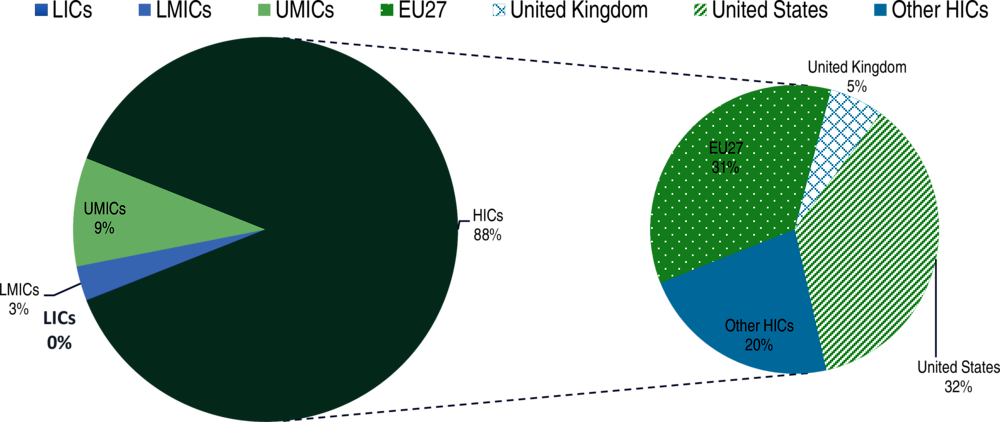
Since early 2022, the global economy has been facing significant headwinds due to Russia’s war in Ukraine that further strain developing countries’ prospects for a strong recovery. The sizeable fiscal stimulus and loose monetary policies put in place in the world’s major economies since the start of the pandemic resulted in the injection of massive liquidity into the economy. While the stimulus helped sustain the global economy in the first stages of the crisis, it also led to a substantial rise in inflation, which reached 6.3% in 2021 compared to an average 4.8% in the previous decade. In addition, the start of Russia’s war against Ukraine, coinciding with the withdrawal of government stimulus measures, contributed to the slowdown of global growth in 2022. The slowdown has widened existing inequalities both within countries (e.g. due to job losses and rising inflation) and across countries, notably increasing developing countries’ divergence from pre-pandemic output projections (Figure 1.1, right side). Due to their specific vulnerabilities, developing countries are incurring the highest output losses from the successive crises. Their cumulated output losses between 2020 and 2023 represent 5% of their pre-pandemic GDP projections; the comparable figure for HICs is only 3%. According to the latest projections, developing countries lost an average USD 1.4 trillion in GDP annually between 2020 and 2023 due to the COVID-19 crisis (IMF, 2020[4]; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 2022[3]). Now, the war could result in an additional loss of approximately USD 718 billion in 2022 and 2023 (IMF, 2022[5]). The accumulating damage wrought by successive crises to developing countries’ economies is translating into significant revenue losses and affecting the composition of their government revenue (Chapter 2).
Before Russia’s full-scale of Ukraine, limited access to vaccines and the relatively small size of their stimulus packages were already hampering the recovery in LICs. While COVID-19 left no country untouched, countries had diverging recovery trajectories in the first two years of the pandemic due to important differences in their response capacity to the health and economic crises. These two factors (access to vaccines and stimulus size) are short-term drivers of the uneven COVID-19 recovery and are correlated with countries’ income levels, reflecting in large part the limited capacity of the poorest countries to confront new and emerging global threats (Table 1.1).
Low and partial vaccine access delayed the economic recovery in developing countries. Despite repeated calls by the World Health Organization (WHO) to ensure global, equitable access to COVID-19 vaccines, the purchase of vaccines was carried out in a largely uncoordinated fashion. By early 2021, HICs had signed purchase agreements to vaccinate their populations several times over while the combination of global supply shortages and vaccine nationalism hindered development partners’ efforts to support developing countries’ access to vaccines through the COVID-19 Vaccines Global Access (COVAX) facility. As a result, only 11% of the population of LICs were fully vaccinated by March 2022 versus more than two-thirds of the population of both HICs (73%) and UMICs (71%) and 47% of the population of LMICs. Countries most in need have been among those lagging furthest behind in terms of vaccine access, including for reasons outlined in Box 1.1. By June 2021, only 1.2% of global COVID-19 vaccine doses had been administered in least developed countries (LDCs) although they are home to 14% of the world’s population (UN, 2022[10]). Recent research shows that had LICs been able to vaccinate their population at the same rate as HICs (i.e. 54% vaccinated by September 2021), they would have increased their GDP by USD 16.27 billion in 2021 (UNDP, 2022[11]) and could have used this foregone income to address the impact of the pandemic or other pressing development challenges.
Already battered by successive shocks, developing countries cannot afford COVID-19 vaccines. It could cost as much as USD 8.4 billion to deliver COVID-19 vaccines to developing country populations, according to a recent report for the United Nations Children’s Fund by (Griffiths et al., 2022[12]). This estimate includes all developing countries except for Bulgaria, the People’s Republic of China (hereinafter China), Romania and Russia and is based on the WHO global vaccination strategy target of vaccinating 70% of the world’s population. Despite the progress achieved through COVAX, which has delivered more than one billion doses of COVID-19 vaccines in developing countries, the funding gap for COVID-19 vaccines is significant. As of 13 June 2022, USD 2.3 billion has been contributed to support the vaccines pillar of the Access to COVID-19 Tools Accelerator – less than half the funding requested and less than a third of the USD 8.4 billion required to deliver COVID-19 vaccines to developing country populations.
Cost is not the only constraint: Developing countries’ limited access to relevant tools and technology hinders COVID-19 vaccine delivery, and there are logistical barriers to local vaccine production (OECD, 2021[13]). Recognising these challenges, the WHO and other partners launched the COVID-19 Technology Access Pool, in May 2020 to allow the developers of COVID-19 vaccines, diagnostics and therapeutics to voluntarily share the intellectual property, knowledge and data. More recently, the June 2022 Ministerial Conference of the World Trade Organization adopted a waiver of certain procedural obligations under the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights to allow the manufacture of COVID-19 vaccines without the consent of the patent owner.
Source: Griffiths et al. (2022[12]), Costs and Predicted Financing Gap to Deliver COVID-19 Vaccines in 133 Low- and Middle-income Countries, https://www.unicef.org/media/114216/file/Costs-and-Predicted-Financing-Gap-to-Deliver-COVID-19-Vaccines-in-133-Low-and-Middle-Income-Countries.pdf; OECD (2021[13]), “Coronavirus (COVID-19) vaccines for developing countries: An equal shot at recovery”, https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/coronavirus-covid-19-vaccines-for-developing-countries-an-equal-shot-at-recovery-6b0771e6/.
Many developing countries also lacked the fiscal and monetary policy space to respond to successive shocks through economic policy support. In the decade prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, many developing countries experienced a deterioration of their fiscal positions as they confronted the successive shocks of the 2008-09 global financial crisis and the 2014 plunge in commodity prices. As a result, many developing countries entered the pandemic with little to no fiscal leeway or spare capacity in their public finances, resulting in wide disparities in countries’ fiscal responses (Figure 1.2). High-income countries were able to mitigate the twin demand and supply shocks by deploying stimulus packages 700 times greater than those of LICs on per capita basis, 86 times greater than in LMIC and 20 times greater than UMICs as shown in Table 1.1. Similarly, strong central bank interventions have mainly occurred only in HICs and UMICs. (Chapter 3 discusses central bank asset purchases following the pandemic in greater detail.) Central banks in many LICs and LMICs, however, had limited margin for manoeuvre to implement accommodative monetary policies due to their lower policy credibility, inability to use quantitative easing and weaker macroeconomic fundamentals.
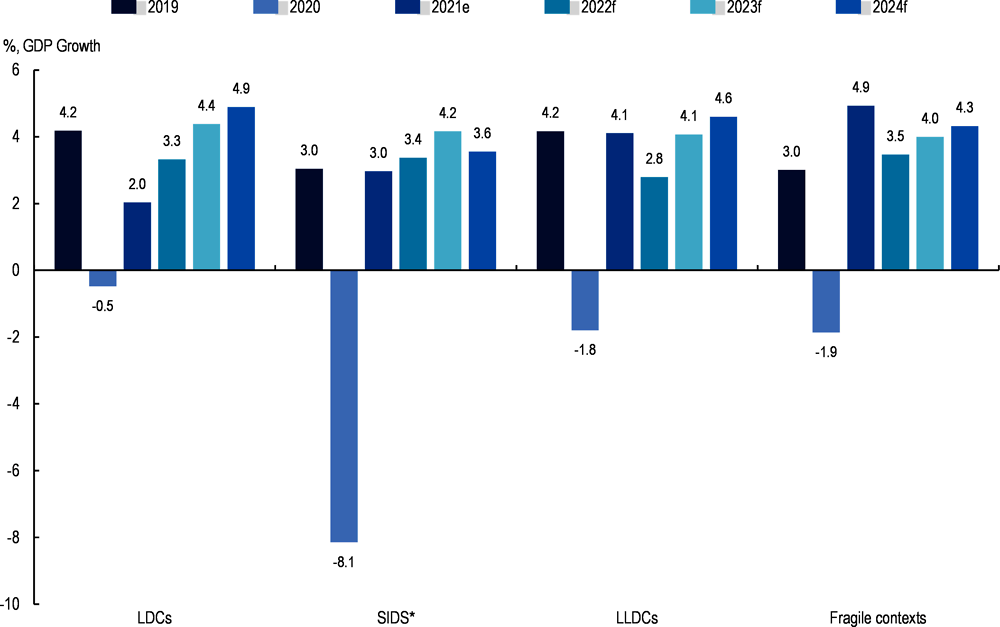
Among countries most in need, small island developing states (SIDS) faced the most severe recession in 2020 as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic but also were able to recover faster than other countries. The GDP of SIDS dropped by -8.6% in 2020, in large part because their economies depend heavily on the tourism sector, which was directly impacted by the travel restrictions and the lockdowns (Figure 1.3). In the same period, GDP dropped -1.9% in fragile contexts, -1.7% in landlocked developing countries (LLDCs) and just -0.5% in LDCs – a less severe impact from the crisis that can be partially explained by the fact they are less connected to the global economy. For example, only 1% of LDCs were in global trade in 2020. On the other hand, SIDS have since been experiencing a stronger recovery than other countries most in need and are forecast to exceed their pre-pandemic growth level in 2022 while GDP growth in LDCs and landlocked countries is not expected to return to pre-pandemic levels before the end of 2023.
The global and country-level economic consequences of the war in Ukraine are further widening disparities between developed and developing countries. Russia’s war against Ukraine is first and foremost a humanitarian catastrophe that has resulted in thousands of casualties and millions of refugees. Chapter 2 describes the implications of this humanitarian crisis for the financing for sustainable development landscape. The conflict has derailed economic projections, which were expected to return to pre-pandemic levels by 2023, while also impacting the livelihoods of people around the world. The war is now expected to reduce global GDP growth by more than 1.5 percentage points in its first full year (OECD, 2022[15]). Recent estimates also suggest the war could increase the global output loss by USD 5.5 trillion between 2020 and 2025 in addition to the International Monetary Fund’s earlier estimate of a USD 12.5 trillion global output loss resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic over this period. LICs stand to lose the most from the effects of the war, as shown in Figure 1.4 (right side), widening the deviation of their GDP growth from pre-pandemic projections. Developing countries are most affected due to the volatility of food and fuel prices as well as by the increased financial uncertainty, which signals risk to investors. At the other end of the income spectrum, the GDP growth of HICs will have nearly caught up with pre-pandemic projections by 2023 despite the war, thanks in large part to massive fiscal and monetary stimulus that have buoyed financial markets.
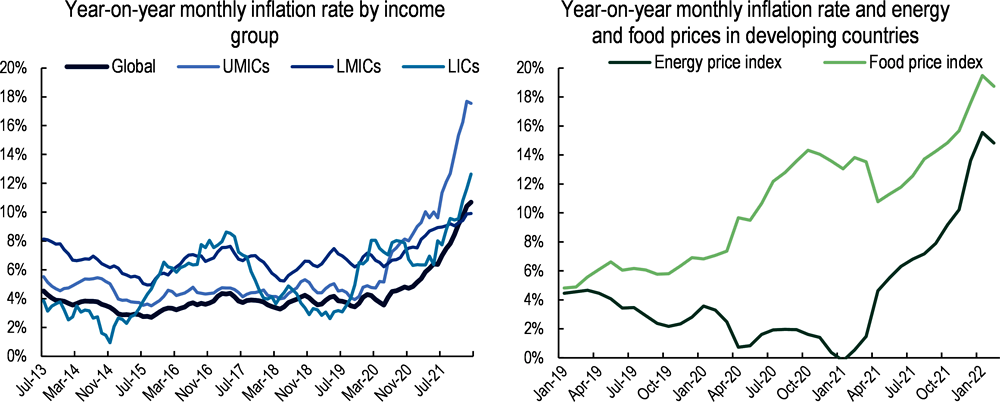
The war is exacerbating global inflationary pressures and contributing to soaring food and energy prices in developing countries. Even before Russia’s full-scale invasion, global consumer prices were on the rise due to supply-demand imbalances caused by the pandemic and the accommodative fiscal and monetary policies put in place in response to the COVID-19 crisis. Inflation in developing countries rose sharply from 2.7% in 2020 to 4.3% in 2021 compared to a milder in global inflation from 2.2% to 3.4% over the same period (Figure 1.4, left side). The war added to these upward pressures due to the weight of Russia and Ukraine as exporters of key commodities. Russia is the world’s largest gas exporter as well as a large global supplier of fertilisers, and the two countries, taken together, account for about one-third of global cereal exports and 44% of Africa’s wheat imports (UNCTAD, 2022[16]). The OECD estimates that, due to the impacts of the Russian invasion, global consumer prices could increase by 2.5 percentage points in the first 12 months of the Ukraine war (OECD, 2022[15]). Moreover, the increased cost of fertilisers and other agricultural inputs means that the surge in food prices could spill over to future years.
Rising consumer prices will hit vulnerable populations the hardest. LICs are especially vulnerable to rising inflation from external shocks. A recent assessment by United Nations Conference on Trade and Development notes that the products likely to cost more due to the war in Ukraine make up more than 5% of the poorest countries’ import baskets but less than 1% of richer countries’ imports (UNCTAD, 2022[16]). In addition, the poorer segments of the world’s population are experiencing larger welfare losses because the war-induced price increases have a greater impact on their real disposable income. Rising global inflation also has implications on the financing for sustainable development landscape (Chapter 2).
1.1.2. Developing economies face heightened financial risks and volatility over the medium to long term
The economic and financial uncertainty generated by mounting geopolitical tensions and the risk of transmission of new adverse shocks to the global economy translate to parallel uncertainty for developing economies. Against this backdrop, business confidence and investor sentiment are likely to remain fragile, possibly depressing investment in developing countries in the medium to long term. The fallout from the war and quantitative tightening are already generating volatility in the financial markets and could ultimately lead to new episodes of capital flight from the poorest countries, with foreign investors turning to safe-haven assets in developed countries. Global market distortions generated by stimulus packages could compound this volatility. As discussed in Chapter 2, these challenges could ultimately translate into higher borrowing costs for developing countries and add to their risk of debt distress. The war and persistent threat of new COVID-19 variants also pose downside risks for global economic activity and could lead to new supply chain disruptions that impact global trade. Countries with insufficient economic diversification – for instance, many LDCs that remain highly dependent on primary commodity exports such as food and fuel – are particularly exposed should the global economy decelerate and affect global demand for certain commodities.
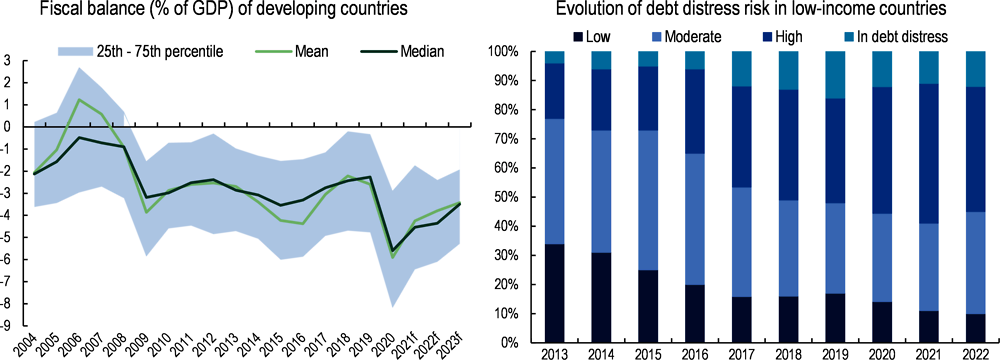
The risk of financial instability in developing countries is at a historic high following multiple economic shocks. The shock of the COVID-19 crisis has further worsened the fiscal vulnerabilities and risk profile of developing countries by adding new pressures on government finances from both the revenue and expenditure sides. The median fiscal balance, or ratio of government revenues to expenditures, in developing countries reached a 20-year low in 2020 of -5.9% of GDP, lower even than these countries’ -3.86% median fiscal balance in the aftermath of the global financial crisis (Figure 1.5, left side). While fiscal balances in developing countries have increased since 2021, owing in part to the increase in certain commodity prices (e.g. food and energy prices), the crash following COVID-19 has hindered an increase to pre-pandemic levels. The accelerating pandemic-era budgetary deficits in developing countries have emerged as a major public policy concern due to the threat they pose to countries’ financial stability, with the risk of debt distress in LICs increasing since the pandemic and some countries at risk of losing access to financial markets or experiencing liquidity crises or sovereign defaults. As shown in Figure 1.5 (right side), the share of LICs in debt distress or at high risk of debt distress has more than doubled since 2013-14 and including between 59% and 55% of LICs in 2021-22. Chapter 3 examines this trend in further detail, in particular the bottlenecks to access sustainable finance in the poorest countries.
Russia’s war against Ukraine casts a shadow over the financing outlook for LICs and other countries most in need. LICs and LDCs are overrepresented in the caseload of countries with macro-fiscal vulnerabilities and excessive exposure to external risks. For example, more than half of LICs (55%) are at high risk of debt distress or already in debt distress as of end of April 2022 (Figure 1.5, right side) and only seven LICs are considered at low risk of debt distress.1 Due to their structural characteristics, LICs are also more vulnerable to external shocks such as the commodity price volatility that followed Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine. Many LICs and LDCs are commodity exporters, tend to derive a significant portion of their revenue from commodity exports and had high levels of debt prior to the pandemic, making them particularly vulnerable to fluctuations of the global economy. In addition, a future acceleration of the green transition may lead to global demand shifting to or away from certain commodities and changes in the valuation of productive assets that would benefit some commodity export-dependent developing countries and harm others.
Prior to the COVID-19 crisis, progress on the 2030 Agenda was insufficient, but low-income and middle-income countries were on a path of slow convergence towards developed countries. In the years prior to the pandemic, developing countries made progress in some key development areas such as poverty reduction, maternal and child health, access to electricity and gender equality, although most countries were off track to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by 2030. In other areas such as reducing inequality, lowering carbon emissions, protecting nature and tackling hunger, progress was stalling and, in some cases, even backsliding. For example, the world remained off track to stay at or below the 1.5°C target set by the 2015 Paris Agreement, and the number of undernourished people at global level increased by 7%, representing an additional 43 million people, between 2014 and 2019 (UN, 2019[19]). Nevertheless, developing countries were on a trend of income convergence towards developed countries, as demonstrated by the upward shift of the growth distribution observed in developing countries since the early 1990s, which contrasts with the stable distribution of growth rates among developed countries.
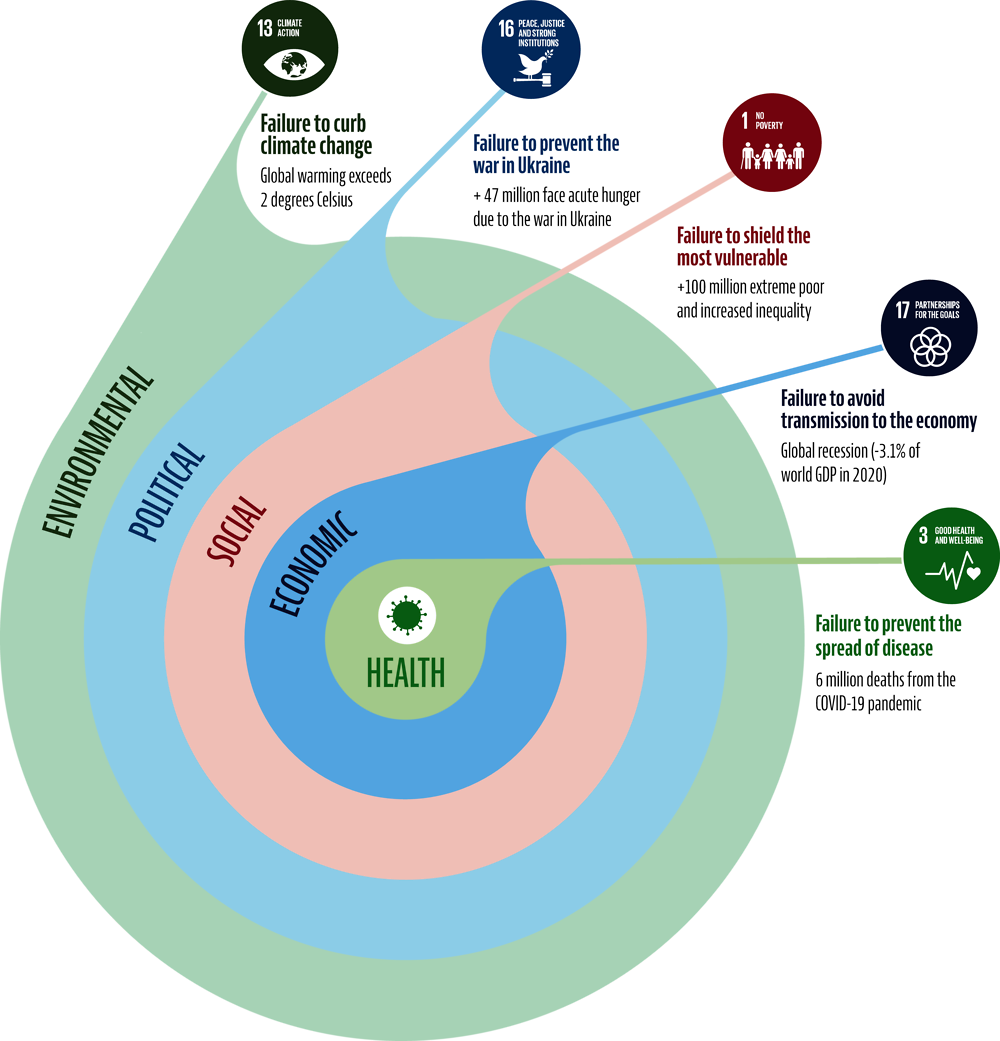
The impact of successive crises could generate a ratchet effect in developing countries, effectively locking them into a protracted recovery. The significant economic and financial effects of the COVID-19 crisis and Russia’s war against Ukraine could impede a return to pre-pandemic development trajectories in developing countries. The pandemic generated a shockwave with huge health, economic and social impacts. Due to the multidimensional nature of the crises, the magnitude of each shock depends on a country’s ability – or failure – to have contained the previous one (Figure 1.6). Governments’ failure to contain the spread of COVID-19 in the early stages of the pandemic, for example, led to a health crisis of global proportions that brought the world economy to a halt, resulting in large economic losses. Governments’ incapacity to shield the most vulnerable from the economic shockwave is now accentuating inequalities and translating into a social crisis. The social wave is likely to have long-run consequences, setting back hard-won SDG progress achieved in the fight against extreme poverty and in the areas of health and education. By straining social and community ties, the social wave of successive crises could turn into a political wave as citizens lose trust in public institutions to provide public goods.
Inaction to avoid the Great Divergence – for instance, failing to stem rising poverty and address inequalities – will increase financing needs to achieve global sustainable development. Front-loading enough resources to curtail the magnifying effect of each crisis wave is the most effective way to avoid future crises. However, the financing needs of developing countries are likely to far exceed the resources available to them. By January 2022, for example, LICs spent on average only USD 8 per capita in social assistance and labour market programmes in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, while the spending of HICs was almost 90 times higher (Gentilini et al., 2022[20]).
1.2.1. Major recent external shocks will leave long-lasting scars on global development and increase the financing needs of the most vulnerable
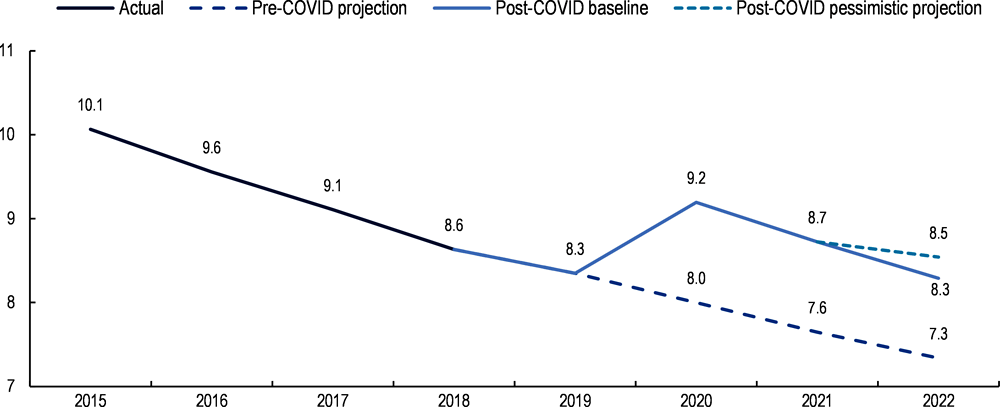
The pandemic and the war in Ukraine mark the end of two decades of decreasing extreme poverty. The pandemic has thrown an additional 97 million people into extreme poverty and jeopardises years of development progress (Gerszon Mahler et al., 2021[21]). While the extreme poverty rate is estimated to have resumed its downward trend in 2021, decreasing from 9.2% in 2020 to 8.7%, the rate remains well above pre-pandemic projections – setting back progress to end global extreme poverty by at least three years – with the rate in 2017 equivalent to the 2020 post-COVID baseline rate (Figure 1.7). The increase in food prices due to the war could push an additional 40 million people into extreme poverty (Center for Global Development, 2022[22]). For example, in Latin America, despite a decrease in total poverty levels between 2020 and 2021, these are projected to increase in 2022 due to rising inflation, especially in food prices. By 2022, 33.7% of the Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC) population could be in poverty and 14.9% in extreme poverty (OECD, forthcoming[23]). Setbacks in the fight against extreme poverty have direct negative consequences at the country and global levels and erode the social, political and economic foundation necessary to achieve other targets. For instance, 98% of respondents to a recent survey, among them experts from 34 developing countries, reported that poverty is a threat to the implementation of other SDGs, with SDGs 3 (good health and well-being), 2 (zero hunger), and 4 (quality education) cited as the most endangered of the goals (Leal Filho et al., 2021[24]). Consequently, extreme poverty stands as an important measure to address the impact of the pandemic, although other indicators provide insightful and necessary information to better assess its implications. In particular, alternative approaches such as multidimensional poverty indices go beyond monetary deprivation and thus place otherwise-overlooked groups and issues at the forefront. This subsection examines the impact on developing countries’ financing needs of successive crises, rising poverty, and soaring between and within-country inequality.
LICs are among the hardest hit by the rise in extreme poverty and the reversal of development gains. The COVID-19 crisis has reversed progress in the fight against extreme poverty by eight to nine years in LICs compared to four to five years in LMICs, five to six years in UMICs and only two to three years in HICs (World Bank, 2021[26]). Despite signs of improvement in 2021 and global poverty decreasing by 2.9% (Gerszon Mahler et al., 2021[21]), the picture remains grim and progress is highly uneven across income groups. The gap between post-COVID poverty levels and pre-COVID projections is largest in LICs, at slightly below four percentage points in the downside scenario for 2022 (Figure 1.8). The main reason for this difference is that expectations of significant poverty reduction did not materialise as a consequence of the pandemic. Although LMICs registered the largest increase in terms of the percentage of population living in extreme poverty in 2020 (+21%), pre-pandemic expectations in terms of poverty reduction were also lower for this income group. The increase in extreme poverty was more limited in UMICs and negligible in HICs, although the use of the poverty threshold at USD 1.90 per day masks the deterioration of living conditions in higher-income countries. Indeed, a recent study of poverty in early 2021 estimated that an average of 69.1 million people would be added to the global poverty headcount for every USD 0.10 per day increase in the USD 1.90 poverty threshold (Summer and Ortiz-Juarez, 2022[27]).
Financing needs in human development such as health and education are growing due to the pandemic and Russia’s war against Ukraine. The priority to respond to COVID-19 left health services saturated, impacting other health outcomes. A WHO review in late 2021 of the continuity of essential health services during the pandemic found substantial disruptions in 90% of countries surveyed (World Health Organization, 2022[29]). More than half the surveyed countries (53% of 80 countries) reported that large shares of the population were still unable to access primary care at the end of 2021. The shift to remote learning when schools closed in the pandemic highlighted digital divides. Students in developing countries – especially girls – lack meaningful connectivity beyond access to the internet (OECD, 2021[30]). Foregone schooling and learning not only negatively affects children’s current well-being but also increases the burden of caring responsibilities, predominantly borne by women. This also is expected to negatively affect human capital accumulation for years to come, with important consequences on future income. Recent estimates suggest that the current generation of students could experience a USD 17 trillion loss of lifetime earnings and that the share of children in low- and middle-income countries with learning poverty, or the percentage of the population with sub-par reading skills at age ten, could rise from the pre-COVID estimation of 50% to 70% (UNESCO/UNICEF/World Bank, 2021[31]). In addition, the combination of income losses and recent food price spikes is threatening food security in many countries. The World Food Programme (2022[32]) estimates that up to 47 million additional people could face acute hunger as a result of the war in Ukraine – a 17% increase over the pre-war baseline of 276 million people who already face acute food insecurity.
At the country level, long-term development setbacks due to income loss will disproportionately affect the financing needs of the most vulnerable, turning the COVID-19 crisis into a pandemic of inequality. The uneven recovery has serious implications for inequalities within developing countries. Due to the skewed impacts of the pandemic on income losses that affect especially low-skill workers, youth and women, inequality in lower-income and middle-income countries is likely to increase. Overall, the shock of the pandemic has had the largest impact on the lowest quintiles of the world’s population. By 2021, the average income of the bottom 40% of the population in developing countries was estimated to be about 2% lower than before the pandemic, with persons with a per capita income between USD 1.99 and USD 5.50 per day being hit the hardest; by 2021, however, the average income of the top 60% of the population in developing countries should return to almost pre-COVID levels (Narayan et al., 2022[33]). Further exacerbating inequalities are differences in access – some of them gender-based – to employment, health care, education, housing and digital technology. Ultimately, the rise of within-country inequalities could become a drag on developing countries’ recovery, spurring a vicious cycle of lower growth and ever-increasing poverty and higher inequalities. Gender-based inequalities risk a similar cycle (Box 1.2). When half of the population is unable to fully contribute to the economy, overall economic recovery and development are hampered.
The pandemic has thrown 42 million women into extreme poverty. Between 2019 and 2021, the number of women living in extreme poverty increased by 11.9%, from 352 to 394 million (UN Women, 2022[34]). This increase is only slightly higher than the one observed for men over the same period (11.5%). However, several studies warn that gender gaps could widen in many development areas, including livelihoods, employment, health and education (UNESCO, 2021[35]).
The COVID-19 crisis has disproportionately impacted women’s employment. One reason is that women are over-represented in low-skill labour activities, especially in the sectors most affected by the pandemic such as accommodation, food services and manufacturing. Furthermore, women were subject to additional pressures given that they represent a large share of the health and care workforce and usually shoulder an additional unpaid care work burden in the household (Azcona et al., 2020[36]). Women working in the informal economy lost 60% of income during the first month of the pandemic (Azcona et al., 2020[37]). Between 2019 and 2020, women’s employment declined by 4.2% at the global level (representing the loss of 54 million jobs) compared to a 3% decline in men’s employment (International Trade Union Confederation, 2021[38]). The gender gap in the employment-to-population ratios increased most in LICs in 2020 (Figure 1.9), and the employment gender gap is expected to persist in the long term. It is now estimated that by 2030, for every 100 men aged 25 to 34 living in extreme poverty, 121 women will be living in similar conditions; prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, the difference was 118 women for every 100 men living in extreme poverty (Azcona et al., 2020[36])..
The crisis will also deepen the gender divide in terms of human development. A recent study estimates that between 11 and 20 million girls will not return to school after the COVID-19 pandemic due to sexual and gender-based violence, unintended pregnancies, forced marriage, and early transitions to work (Kwauk, Schmidt and Ganju, 2021[39]).
Source: UN Women (2022[34]), “Stories: Poverty deepens for women and girls, according to latest projections", https://data.unwomen.org/features/poverty-deepens-women-and-girls-according-latest-projections; (UNESCO, 2021[35]), #HerEducationOurFuture: Keeping Girls in the Picture During and After the COVID-19 Crisis, https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000375707; (Azcona et al., 2020[36]), From Insights to Action: Gender Equality in the Wake of COVID-19, https://www.unwomen.org/sites/default/files/Headquarters/Attachments/Sections/Library/Publications/2020/Gender-equality-in-the-wake-of-COVID-19-en.pdf; Azcona et al., (2020[37]), Will the Pandemic Derail Hard-won Progress on Gender Equality?,https://www.unwomen.org/sites/default/files/Headquarters/Attachments/Sections/Library/Publications/2020/Spotlight-on-gender-COVID-19-and-the-SDGs-en.pdf; International Labour Organization (2021[38]), An Uneven and Gender-unequal COVID-19: Update on Gender and Employment Trends, https://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---ed_emp/documents/publication/wcms_824865.pdf; Kwauk, Schmidt and Ganju (2021[39]), “What do we know about the effects of COVID-19 on girls’ return to school?”, https://www.brookings.edu/blog/education-plus-development/2021/09/22/what-do-we-know-about-the-effects-of-covid-19-on-girls-return-to-school/.
1.2.2. Achieving a recovery aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals will require financing for both rescue and recovery measures
Developing countries lack both short-term rescue and long-term recovery financing to achieve sustainable development. Developing countries faced acute challenges to deliver emergency financing and support to respond to COVID-19 as well as to commit to longer-term investments to build back better (BBB). As a percentage of GDP, fiscal support measures in 2021-22 for rescue and recovery were on average 3 and 6 times lower respectively in low- and middle-income countries than in HICs (Figure 1.10). Rescue-type measures include short-term emergency support such as liquidity support, welfare transfers, and tax relief to the households and firms most impacted by the successive health, economic, climate and geopolitical crises. Recovery-type measures, including policy incentives and investments, provide long-term support to boost economic growth.
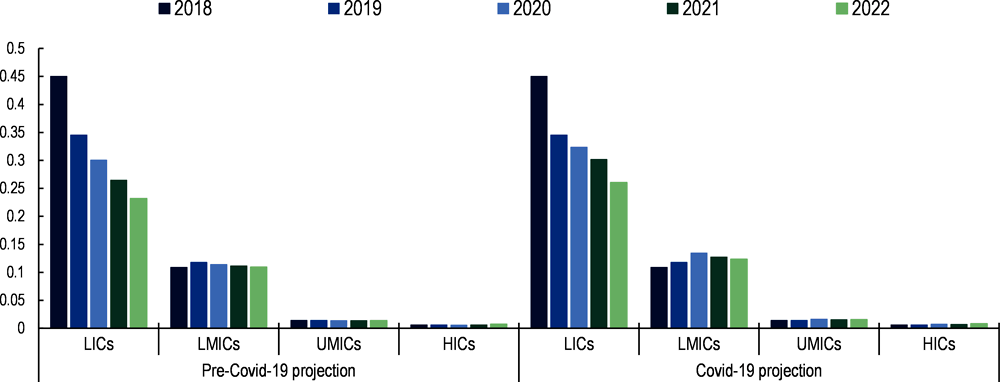
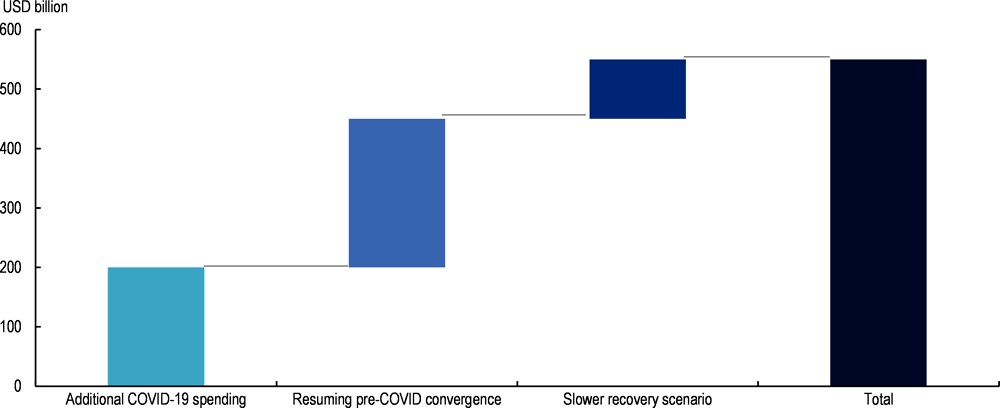
Rescue and recovery financing needs are particularly high in the poorest countries. The additional COVID-19 financing required by LICs between 2021 and 2025 is estimated at USD 450 billion (Figure 1.11) (IMF, 2021[41]). This amount includes USD 200 billion of additional COVID-19 spending to step up the response to the crisis and build financial buffers as well as USD 250 billion to put LICs back on their pre-pandemic trajectory of convergence with advanced economies. An additional USD 100 billion could be required if some risks – such as slower-than-expected vaccine rollouts or a worsening of the pandemic due to new variants – materialise and lead to an even slower recovery in LICs. The amount of financing required by Cambodia, Nigeria, Pakistan and Rwanda in five SDG sectors (education, health, roads, electricity, and water and sanitation) increased by 21% on average as a result of the COVID-19 crisis (Benedek et al., 2021[42]). It should be noted that these studies on financing needs in LICs were published prior to Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine and did not take into account the additional financing needs the war will engender. Chapter 2 provides a more detailed overview of the SDG financing gap in terms of financing flows and addresses the two-fold impact of the successive crises through increased government spending and lower domestic and external financing.
The sustainability boom in HICs could lead to a sustainability crunch in the developing world. Over the past two years, developed countries have launched a series of initiatives and stimulus packages to boost the recovery and put their economies on a sustained growth path. Many of these initiatives, such as the Biden administration’s proposed USD 1.9 trillion Build Back Better Act and the European Union’s USD 2 trillion NextGenerationEU, include a specific focus on green investments and aim to make their societies more inclusive and resilient to future shocks. The OECD is also calling for a “quality” recovery that responds to four criteria: strong, inclusive, green and resilient (OECD et al., 2021[43]). However, caution is required to ensure that the proliferation of regulations, standards and norms does not further increase inequalities in access to financing for sustainable development. Early evidence suggests that in the absence of a clear strategy to ensure that developing countries benefit from the BBB agenda, a number of developing countries could be left behind due to a lack of capacity to demonstrate compliance with increasing sustainability standards (OECD/WBG, forthcoming[44]). Chapter 3 discusses in depth the need for policy coherence and concrete actions to ensure a sustainable and equitable recovery.
Limited fiscal space in developing countries may further prevent them from BBB. Amid historic development setbacks, widening inequalities, a lingering pandemic, and new adverse shocks such as the surge in food and commodity prices, developing countries need to balance a growing number of priorities. Given the limited resources available to them, this balance requires clear prioritisation of short-term spending (e.g. to deploy emergency support measures) and longer-term investments (e.g. to build sustainable and resilient infrastructure, strengthen health and education systems, or restore financial buffers to preserve the credibility of their fiscal frameworks). Due to the limited fiscal space of developing countries and their need to respond to successive crises, there is a risk that short-term relief measures could end up crowding out much-needed investment necessary for a green, resilient and inclusive recovery. A short-sighted view could also prompt governments to favour investments with lower upfront costs to the detriment of better economic returns in the long run. Box 1.3 examines the cost-efficiency returns of financing BBB strategies in developing countries.
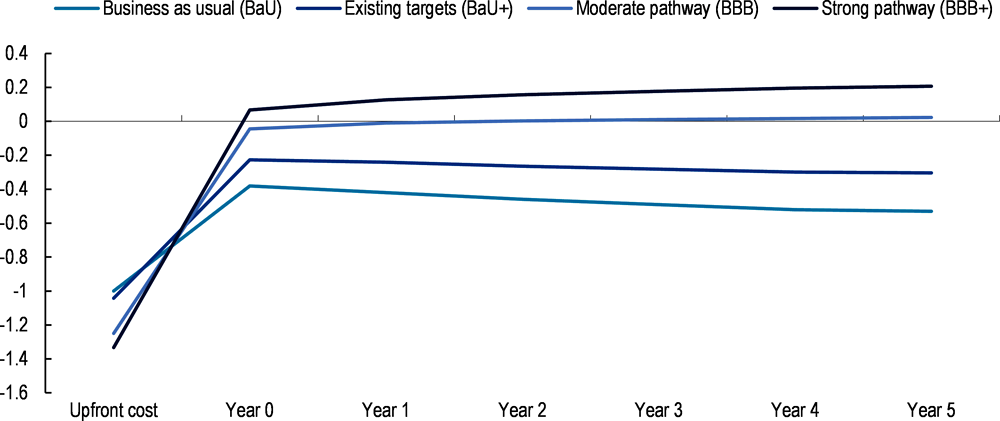
The resource-constrained environment facing developing countries in the aftermath of the COVID-19 crisis calls for consideration of the cost-effectiveness of BBB strategies. Investing in the green, resilient and inclusive recovery called for by world leaders requires a shift in the allocation of resources. The green transition, for example, requires more capital-intensive technologies (e.g. renewable energy and climate-resilient infrastructure) and is thus likely to result in higher upfront costs. The question is whether this higher cost is compensated for by better returns over time or whether the cost may lead to trade-offs among developing countries’ goals of economic development, sustainability, inclusiveness and resilience.
The energy sector provides an illustration of the economic benefits that can result from investing in a sustainable recovery. Recent research shows that investments in green (renewable) energy infrastructure have a stronger and more sustained impact on countries’ GDP than investments in non-renewable energy infrastructure (Batini et al., 2021[45]). The results indicate that each additional US dollar invested in green energy infrastructure crowds in another 53 cents over a period of four years following the investment. On the other hand, additional investment in non-renewable energy infrastructure appears to crowd out other GDP components (consumption, investment, net exports) in the medium term.
Evidence from the energy sector points to the cost-effectiveness of BBB despite its higher upfront costs. Depending on the climate objective scenario used, the upfront costs of investing in green infrastructure could be up to 33% higher than for conventional energy infrastructure investment (Rozenberg and Fay, 2019[46]). In other words, for each US dollar invested under a business-as-usual (BaU) scenario, the cost of a similar investment in green energy infrastructure could amount to as much as USD 1.33. However, the strong positive impact on GDP observed for green investment more than offsets the initial higher investment costs (Figure 1.12) and provides a positive return for countries’ GDP (unlike in the BaU scenarios).
These results confirm the importance of ensuring that developing countries with the fewest resources benefit from the cost-efficiency gains of the BBB agenda. HICs will likely need to consider how to support a sustainable recovery abroad (i.e. in their partner countries). Despite the economic benefits of BBB, recent research suggests that some new BBB policies (e.g. for climate mitigation) could impose a financial burden on the global poor through increased energy and food prices (Soergel et al., 2021[47]). This burden could be offset through redistributive policies at the country and international level – for example, by meeting the commitment made during the 15th session of the Conference of the Parties to provide USD 100 billion per year of climate finance to developing countries. Chapter 3 assesses the extent to which financing and BBB strategies to ensure sustainability are aligning to the SDGs to avoid zero-sum trade-offs across the goals and promote equity to mitigate transmission of risks across countries.
Source: Batini et al. (2021[45]), “Building back better: How big are green spending multipliers?”, https://doi.org/10.5089/9781513574462.001; Rozenberg and Fay (2019[46]), Beyond the Gap: How Countries Can Afford the Infrastructure They Need while Protecting the Planet, https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/31291; Soergel et al. (2021[47]), “Combining ambitious climate policies with efforts to eradicate poverty”, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-22315-9
The economic shock of successive crises have increased the SDG financing needs and call for concerted effort to ensure sufficient financing to BBB and avoid the Great Divergence in the poorest countries. The uneven recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic and the consequences of the war in Ukraine place unprecedented pressure on policy makers already struggling to balance short- and long-term financing for sustainable development priorities. Pre-existing constraints exacerbated by successive crises have further reduced the availability of financing in countries most in need of resources to invest in a just and sustainable recovery. Chapter 2 points to a growing SDG financing gap and potential tipping point in the financing for the sustainable landscape. It outlines the state of domestic, external, public and private financing flows to developing countries and the resources that are available to meet the growing financing needs discussed in Chapter 1.
References
[37] Azcona, G. et al. (2020), Will the Pandemic Derail Hard-won Progress on Gender Equality?, UN Women, New York, https://www.unwomen.org/sites/default/files/Headquarters/Attachments/Sections/Library/Publications/2020/Spotlight-on-gender-COVID-19-and-the-SDGs-en.pdf.
[36] Azcona, G. et al. (2020), From Insights to Action: Gender Equality in the Wake of COVID-19, UN Women, New York, https://www.unwomen.org/sites/default/files/Headquarters/Attachments/Sections/Library/Publications/2020/Gender-equality-in-the-wake-of-COVID-19-en.pdf.
[45] Batini, N. et al. (2021), “Building Back Better: How Big Are Green Spending Multipliers?”, IMF Working Papers, Vol. 2021/087, p. 1, https://doi.org/10.5089/9781513574462.001.
[42] Benedek, D. et al. (2021), A Post-Pandemic Assessment of the Sustainable Development Goals, International Monetary Fund, Washington, DC, https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/Staff-Discussion-Notes/Issues/2021/04/27/A-Post-Pandemic-Assessment-of-the-Sustainable-Development-Goals-460076.
[22] Center for Global Development (2022), Extreme Poverty Estimate Following Russia’s Invasion of Ukraine (Mid-March 2022), https://cgdev.org/sites/default/files/2022-04/background%20price%20spike%20analysis.pdf.
[20] Gentilini, U. et al. (2022), Social Protection and Jobs Responses to COVID-19: A Real-Time Review of Country Measures, World Bank, Washington, DC, https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/37186.
[25] Gerszon Mahler, D. et al. (2022), “Pandemic, prices, and poverty”, World Bank Data Blog, https://blogs.worldbank.org/opendata/pandemic-prices-and-poverty.
[21] Gerszon Mahler, D. et al. (2021), “Updated estimates of the impact of COVID-19 on global poverty: Turning the corner on the pandemic in 2021?”, World Bank Data Blog, https://blogs.worldbank.org/opendata/updated-estimates-impact-covid-19-global-poverty-turning-corner-pandemic-2021.
[12] Griffiths, U. et al. (2022), Costs and Predicted Financing Gap to Deliver COVID-19 Vaccines in 133 Low- and Middle-income Countries, United Nations Children’s Fund, New York, https://www.unicef.org/media/114216/file/Costs-and-Predicted-Financing-Gap-to-Deliver-COVID-19-Vaccines-in-133-Low-and-Middle-Income-Countries.pdf.
[17] Ha, J., M. Kose and F. Ohnsorge (2021), “One-stop source: A global database of inflation”, Policy Research Working Paper, No. 9737, https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/36037.
[18] IMF (2022), Interactive Guide on Debt Sustainability Analysis Low-Income Countries (interactive guide), International Monetary Fund (IMF), Washington, DC, https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/DSA (accessed on 1 June 2022).
[5] IMF (2022), World Economic Outlook, April 2022: War Sets Back the Global Recovery, International Monetary Fund (IMF), Washington, DC, https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/Issues/2022/04/19/world-economic-outlook-april-2022.
[9] IMF (2021), Fiscal Monitor Database of Country Fiscal Measures in Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic (database), International Monetary Fund (IMF), Washington, DC, https://www.imf.org/en/Topics/imf-and-covid19/Fiscal-Policies-Database-in-Response-to-COVID-19 (accessed on January 2022).
[41] IMF (2021), Macroeconomic Developments and Prospects in Low-Income Countries--2021, International Monetary Fund (IMF), Washington, DC, https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/Policy-Papers/Issues/2021/03/30/Macroeconomic-Developments-and-Prospects-In-Low-Income-Countries-2021-50312.
[4] IMF (2020), World Economic Outlook - Update: Tentative Stabilization, Sluggish Recovery?, International Monetary Fund (IMF), Washington, DC, https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/Issues/2020/01/20/weo-update-january2020.
[3] Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (2022), Climate Change 2022 - Mitigation of Climate Change: Summary for Policymakers, https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg3/.
[38] International Trade Union Confederation (2021), Investments in Social Protection and Their Impacts on Economic Growth, https://www.ituc-csi.org/IMG/pdf/investments_in_social_protection_and_their_impacts_on_economic_growth.pdf.
[39] Kwauk, C., D. Schmidt and E. Ganju (2021), “What do we know about the effects of COVID-19 on girls’ return to school?”, Brookings Education Plus Development Blog, https://www.brookings.edu/blog/education-plus-development/2021/09/22/what-do-we-know-about-the-effects-of-covid-19-on-girls-return-to-school/.
[24] Leal Filho, W. et al. (2021), “Poverty: A central barrier to the implementation of the UN Sustainable Development Goals”, Environmental Science & Policy, Vol. 125, pp. 96-104, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2021.08.020.
[33] Narayan, A. et al. (2022), “COVID-19 and economic inequality: Short-term impacts with long-term consequences”, Policy Research Working Paper, No. 9902, World Bank Group, Washington, DC, https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/219141642091810115/pdf/COVID-19-and-Economic-Inequality-Short-Term-Impacts-with-Long-Term-Consequences.pdf.
[40] O’Callaghan, B., E. Murdoch and N. Yau (2021), Global Recovery Observatory: Draft Methodological Document, Smith School of Enterprise and the Environment, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK, https://recovery.smithschool.ox.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/20210201-Global-Recovery-Observatory-Draft-Methodology-Document-.pdf.
[15] OECD (2022), OECD Economic Outlook, Interim Report March 2022: Economic and Social Impacts and Policy Implications of the War in Ukraine, OECD Publishing, Paris, https://doi.org/10.1787/4181d61b-en.
[13] OECD (2021), “Coronavirus (COVID-19) vaccines for developing countries: An equal shot at recovery”, OECD Policy Responses to Coronavirus (COVID-19), https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/coronavirus-covid-19-vaccines-for-developing-countries-an-equal-shot-at-recovery-6b0771e6/.
[30] OECD (2021), Development Co-operation Report 2021: Shaping a Just Digital Transformation, OECD Publishing, Paris, https://doi.org/10.1787/ce08832f-en.
[2] OECD (2021), Taxing Energy Use for Sustainable Development: Opportunities for Energy Tax and Subsidy Reform in Selected Developing and Emerging Economies, OECD Publishing, Paris, https://www.oecd.org/tax/tax-policy/taxing-energy-use-for-sustainable-development.htm.
[1] OECD (2020), Global Outlook on Financing for Sustainable Development 2021: A New Way to Invest for People and Planet, OECD Publishing, Paris, https://doi.org/10.1787/e3c30a9a-en.
[23] OECD (forthcoming), Latin American Economic Outlook: towards a green and just transition.
[44] OECD/WBG (forthcoming), VAT Digital Toolkit for Africa, OECD Publishing, Paris.
[43] OECD et al. (2021), VAT Digital Toolkit for Latin America and the Caribbean, OECD Publishing, Paris, https://www.oecd.org/tax/consumption/vat-digital-toolkit-for-latin-america-and-the-caribbean.pdf.
[46] Rozenberg, J. and M. Fay (2019), Beyond the Gap: How Countries Can Afford the Infrastructure They Need while Protecting the Planet, World Bank, Washington, DC, https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/31291.
[47] Soergel, B. et al. (2021), “Combining ambitious climate policies with efforts to eradicate poverty”, Nature Communications, Vol. 12/1, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-22315-9.
[27] Summer, A. and E. Ortiz-Juarez (2022), “Above or below the poverty line: Three key questions for understanding shifts in global poverty”, Wider Angle Blog, https://www.wider.unu.edu/publication/above-or-below-poverty-line.
[10] UN (2022), Vaccination and COVID-19 Funding for Least Developed Countries, Office of the High Representative for the Least Developed Countries, Landlocked Developing Countries and Small Island Developing States, United Nations, New York, https://www.un.org/ohrlls/content/covid-19-ldcs (accessed on 1 April 2022).
[19] UN (2019), The Sustainable Development Goals Report, https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2019/The-Sustainable-Development-Goals-Report-2019.pdf.
[34] UN Women (2022), Stories: Poverty deepens for women and girls, according to latest projections, https://data.unwomen.org/features/poverty-deepens-women-and-girls-according-latest-projections.
[16] UNCTAD (2022), UNCTAD Rapid Assessment: The Impact on Trade and Development of the War in Ukraine, United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), Geneva, https://unctad.org/system/files/official-document/osginf2022d1_en.pdf.
[11] UNDP (2022), State of INFFs, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), New York, https://inff.org/news/2022-state-of-inffs-86-countries-advance-inffs-to-finance-sustainable-development.
[35] UNESCO (2021), #HerEducationOurFuture: Keeping Girls in the Picture During and After the COVID-19 Crisis, https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000375707.
[31] UNESCO/UNICEF/World Bank (2021), The State of the Global Education Crisis: A Path to Recovery, https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/416991638768297704/pdf/The-State-of-the-Global-Education-Crisis-A-Path-to-Recovery.pdf.
[28] World Bank (2022), DataBank - Population estimates and projections (database), https://databank.worldbank.org/source/population-estimates-and-projections.
[6] World Bank (2022), Global Economic Prospects, June 2022, The World Bank, https://doi.org/10.1596/978-1-4648-1843-1.
[26] World Bank (2021), Poverty, Median Incomes, and Inequality in 2021: A Diverging Recovery, https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/936001635880885713/pdf/Poverty-Median-Incomes-and-Inequality-in-2021-A-Diverging-Recovery.pdf.
[7] World Bank Group (2020), Global Economic Prospects: Slow Growth, Policy Challenges, https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/33044/9781464814693.pdf.
[14] World Economic Forum (2022), “Here’s Why Developed Economies Must Bear the $100 Trillion Cost of the Net-Zero Transition in Emerging Markets”, World Economic Forum Agenda, https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2022/04/emerging-developed-economies-net-zero-transition/#:~:text=According%20to%20the%20bank's%20calculations,year%20between%202021%20and%202060.
[32] World Food Programme (2022), Projected Increase in Acute Food Insecurity Due to War in Ukraine, https://docs.wfp.org/api/documents/WFP-0000138289/download/.
[29] World Health Organization (2022), Third Round of the Global Pulse Survey on Continuity of Essential Health Services During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Interim Report November-December 2021, https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-EHS_continuity-survey-2022.1.
[8] World Health Organization (2022), WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard (database), https://covid19.who.int/table (accessed on 22 March 2022).
Note
← 1. These figures are based on the April 2022 debt sustainability analyses of the World Bank and International Monetary Fund. See https://www.imf.org/en/publications/dsa.