Germany
This chapter includes data on the income taxes paid by workers, their social security contributions, the family benefits they receive in the form of cash transfers as well as the social security contributions and payroll taxes paid by their employers. Results reported include the marginal and average tax burden for eight different family types.
Methodological information is available for personal income tax systems, compulsory social security contributions to schemes operated within the government sector, universal cash transfers as well as recent changes in the tax/benefit system. The methodology also includes the parameter values and tax equations underlying the data.
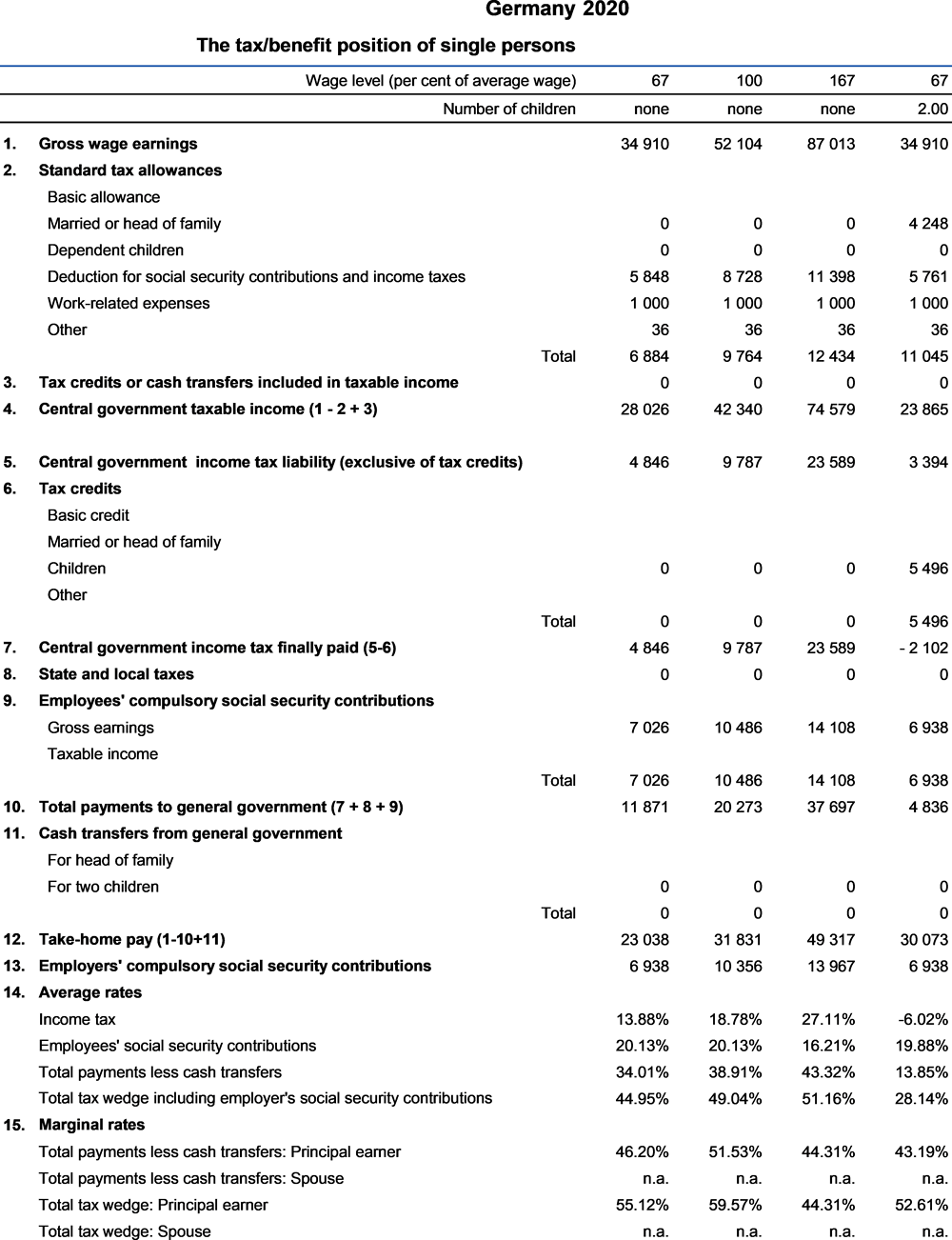
The national currency is the Euro (EUR). In 2020, EUR 0.88 was equal to USD 1. The average worker earned EUR 52 104 (Secretariat estimate).
1.1. Central/federal government income taxes
1.1.1. Tax unit
Spouses may choose between two options: Joint assessment or individual assessment. The vast majority of couples benefits financially from the joint assessment by minimizing the tax burden of the household. The income of dependent children is not assessable with that of the parents. The calculations in this Report are therefore based on the assumption of joint taxation for spouses.
1.1.2. Tax allowances and tax credits:
1.1.2.1. Standard reliefs and work related expenses
Standard marital status reliefs: In the case of joint assessment, specific allowances are doubled. The income tax liability for spouses who are assessed jointly is computed as follows:
Results: Given the progressive income taxation the resulting tax liability for the household is lower than the sum of individual taxation. The household as a unit benefits from this solution otherwise both parts of the couple would opt out. Principal and second earners have the same average and marginal income tax rates.
The splitting effect decreases by increasing convergence of the incomes of principal earner and the spouse.
Relief(s) for children: In 2020, there are increased tax credits of EUR 2 448 for the first and the second child, of EUR 2 520 for the third child and of EUR 2 820 for the fourth and subsequent children. There is a tax allowance of EUR 2 586 for the subsistence of a child and an additional EUR 1 320 for minding and education or training needs (EUR 3 906). The amount of this allowance is doubled in case of jointly assessed parents. If the value of the tax credit is less than the relief calculated applying the tax allowances, the taxpayer obtains the tax allowance instead of the tax credit. It is also doubled for lone parents in cases where the other parent does not pay alimony. This is the assumption in the calculations presented in this Report.
In 2020, families with children will receive a one-time bonus benefit payment of EUR 300 per child. The bonus will not be offset against basic income support for jobseekers. However, in the case of households with higher incomes, the bonus will be offset against the tax allowance for children.
Relief for lone parents: As of 1 January 2015, taxpayers who live alone with at least one child that entitles them to the tax allowances or tax credits for children, receive a standard additional allowance of EUR 1 908 (formerly EUR 1 308). This additional allowance is increased by EUR 240 for each child in case of more than one child living in the household.
The standard tax allowance for lone parents will be raised temporarily to EUR 4 008 in the years 2020 and 2021 in order to stabilise the income of single parents.
Reliefs for social security contributions and life insurance contributions: Social security contributions and other expenses incurred in provision for the future (e.g. life insurance) are deductible up to specific ceilings. In 2005, a new calculation scheme came into force:
Step 1: all contributions made to pension funds (i.e. both employee’s and employer’s contributions) are added up. Step 2: the resulting amount is limited to the equivalent of the maximum contribution rate to miners’ pension insurance scheme, rounded up to the nearest euro (in 2020: EUR 25 046). Step 3: a certain percentage is applied to this amount (starting from 60% in 2005, this percentage will be increased by 2 percentage points each year; it will reach 100% in 2025). Step 4: the resulting amount, diminished by the (tax-free) contributions of the employer, is deductible from income.
The tax treatment of social security expenses (health, unemployment and care insurance) changed as of 1 January 2010. Employees’ annual contributions to statutory health insurance excluding sickness benefit (assumed to amount to 96% of statutory health contributions) and employees’ contributions to mandatory long-term care insurance are deductible from the tax base. In case these contributions do not exceed EUR 1 900/3 800 (single/married couples), contributions to unemployment insurance and other insurances premiums can be deducted in addition up to this ceiling.
Work related expenses: EUR 1 000 lump sum allowance per gainfully employed person.
Special expenses: Lump sum allowance (EUR 36/72 (singles/couples)) for special expenses, e.g. for tax accountancy. The actual expenses will be fully deductible from taxable income if the taxpayer proves that these expenses exceed the lump sum allowance.
1.1.2.2. Main non-standard tax reliefs applicable to an AW
Contributions to pensions, life insurance, superannuation schemes: Other expenses than the compulsory contributions to social security are deductible as reliefs for (voluntary) social security contributions up to specific ceilings (see section 1.1.2.1.).
Medical expenses: Partially deductible if not covered by insurance.
Other: Work related expenses that exceed the lump-sum allowance are fully deductible (no ceiling).
1.1.3. Tax schedule
The German tax schedule is formula based. Taxable income is rounded down (to the EUR).
The income tax liability (amounts in EUR) is calculated as follows:
These formulas are used to calculate the income tax for single individuals and married couples too.
If families choose the option of being assessed separately these formulas are applied to the individual taxable income of the principal earner and the spouse. In the case of jointly assessed families these rates are applied to half of the joint taxable income (see point 1.1.2.1. Splitting method).
1.1.4. Solidarity surcharge
The solidarity surcharge is levied at 5.5% of the income tax liability subject to an exemption limit of EUR 972/1 944 (singles/couples). The income tax liability is calculated applying the tax allowance for children. If the income tax liability exceeds the exemption limit, the solidarity surcharge will be phased in at a higher rate of 20% of the difference between the income tax liability and the exemption limit until it equals 5.5% of the total liability.
The amount of social security contributions depends on the wage and the insurance contribution rate. All contributions are subject to a contribution ceiling, i.e. the maximum income for which statutory insurance contributions are calculated. The contribution rates for pension, health, care and unemployment insurances are fixed by the government.
2.1. Employees’ contributions
In general, earnings up to EUR 4 800 per year were free of employee social security contributions until 31 December 2012. As of 1 January 2013, some essential changes came into effect concerning minimally paid employment. The earnings limit increased from EUR 400 to EUR 450 per month. Persons whose mini-job started before 2013 and do not exceed the previous earnings limit of EUR 400 stay contribution-free in all classes of social insurance. Otherwise, persons who take up a new mini-job are generally subject to mandatory insurance coverage in the statutory pension scheme with the full pension contribution rate of 18.6% (in 2020). If the earnings are below the amount of EUR 175 (minimum contribution limit), a minimum contribution of EUR 32.55 has to be paid (18.6% of EUR 175). The employer’s share amounts to 15% of the whole pay whereas the employee’s part adds up to 3.6% (or the difference between minimum contribution and employer share). By applying for an exemption from obligatory insurance coverage the mini-job holder may reduce his share to EUR 0.
As of 1 April 2003, there was an additional concession for employees with monthly income between EUR 400.01 and EUR 800 per month (the so-called ‘sliding pay scale’, EUR 4 800.12 and EUR 9 600 per year). Due to the new regulations mentioned above the earnings limits shifted to EUR 450.01 and EUR 850.00 per month (EUR 5 400.12 and EUR 10 200 per year). As of 1 July 2019, provisions for the newly-created so-called ‘transition band’ extend the upper earnings limit from EUR 850 per month to EUR 1 300 per month (EUR 15 600 per year). If the employee’s income falls within this range, part of the income is exempt from social insurance contributions. However, employers are still required to pay the regular contributions on the employee’s earnings. The arrangement is purely intended to relieve the financial burden on employees. The employees’ contributions to social insurance rise on a straight-line basis over the income band reaching the full rate at EUR 1 300 per month . Within the ‘transition band’, employees’ reduced contribution rates to statutory pension insurance will not minimise their pension entitlements any more. Details on social security contributions for workers earning more than EUR 15 600 per year are provided below.
2.1.1. Pensions
Employers and employees pay each half of the contribution rate of 18.6% in 2020, that is 9.3% of the employee’s gross wage earnings, up to a contribution ceiling of EUR 82 800.
2.1.2. Sickness
As of 1 January 2015, the applicable contribution rate is 14.6% on principle (portion of 7.3% for employers and employees). Depending on the financial situation of each sickness fund, employees only were obliged to pay a supplementary contribution to the sickness fund until December 2018. Since January 2019, employees and employers have been required to pay part of this supplementary contribution which amounts to 1.1% on average in 2020 (portion of 0.55% for employers and employees). Therefore, the contribution rate averages 7.85% for employees and employers in 2020. The contribution ceiling in 2020 is EUR 56 250. While all calculations shown in this Report assume membership in the public health insurance, workers with earnings above the contribution ceiling may opt out of the mandatory public health insurance system and may choose a private insurance provider instead (those opting for a private health insurance provider are required to obtain private long-term care insurance as well).
2.1.3. Unemployment
Employees pay half of the insurance contributions; the employer pays the other half. In 2020, the contribution rate is 2.4% of assessable income. Employee and employer each pay 1.2%. The contribution ceiling is EUR 82 800.
2.1.4. Care
A long-term care insurance (a 1% contribution rate) went into effect on 1 January 1995. The rate was raised to 1.7% of the gross wage when home nursing care benefits were added six months later. As of 1 July 2008, the rate was increased to 1.95%. In 2013 and 2014, the contribution rate amounted to 2.05%. In 2015 and 2016, the contribution rate added up to 2.35%. As of 1 January 2017, the contribution rate was augmented to 2.55%. Since January 2019, the contribution rate has amounted to 3.05%.The employers pay half of the contributions for long-term care insurance. In other words, employers and employees both pay a rate of 1.525%. The assessable income is scaled according to the gross wage earnings but there is a contribution ceiling of EUR 56 250 in 2020.
As from 1 January 2005, child-raising is given special recognition in the law relating to statutory long-term care insurance. Childless contribution payers are required to pay a supplement of 0.25%, raising the contribution rate paid by a childless employee from 0.975% to 1.225% as of 1 July 2008. In 2013 and 2014, the contribution rate of a childless employee added up to 1.275%. In 2015 and 2016, the contribution rate amounted to 1.425% for a childless employee. As of 1 January 2017, the contribution rate was raised to 1.525% for a childless employee. Since January 2019, a childless employee has had to pay a contribution rate of 1.775%.
2.2. Employers’ contributions
2.2.2. Work injury
Germany has established a statutory occupational accident insurance. It is provided by industrial, agricultural and public-sector employers’ liability insurance funds. This insurance protects employees and their families against the consequences of accidents at work and occupational illnesses. It is funded through the contributions paid by employers only. The amount of the employer’s contributions depends on the sum total of employee’s annual pay and the employer’s respective hazard level. As it is not possible to identify a representative contribution rate, these amounts are not considered in this Report.
The following table shows changes in the tax credit and the tax allowance for children since 1997:
Up to 2004, the calculation of the relief for social security contributions and other expenses proceeded in three steps. First, EUR 3 068/6 136 (singles/couples) was deducted. These amounts were, however, lowered by 16% of gross wages (serving as a proxy for employers’ social security contributions). This deduction was provided as a partial compensation for the self-employed who do not receive tax-free employers’ social security contributions. Second, the remaining expenses were deductible up to EUR 1 334/2 668 (singles/couples). Third, half of the remaining expenses were deductible up to EUR 667/1 334 (singles/couples).
In 2004, the tax rate was reduced and the formula for calculating the income tax was changed. The relief for lone parents was reduced to EUR 1 308, the lump sum allowance for work related expenses was reduced to EUR 920.
As from 1 January 2005, the final stage of the 2000-tax reform came into effect. The bottom and top income tax rates were further reduced to 15% and 42%. Since 1998, both the bottom and top income tax rate have been reduced by about 11 percentage points while the personal allowance has been raised from EUR 6 322 to EUR 7 664. The tax cuts reduce the tax burden for all income taxpayers, affording the greatest relief to employees and families with low and medium incomes as well as to small- and medium-sized unincorporated businesses.
On 1 January 2005, the law regulating the taxation of pensions and pension expenses entered into force. The law provides a gradual transition to ex-post taxation of pensions paid by the statutory pensions insurance. In the long run, the tax treatment of capital-based employee pension schemes based on a contract between employer and employee will be reformed in the same way as the tax treatment in respect of the state pension scheme. In addition to the increased deductibility of contributions to the state and certain private pension schemes, the law contains rules which are intended to increase the attractiveness of private capital-based pension schemes and to encourage individuals to invest privately for their old-age pension.
Up to 30 June of 2005, employees paid half of the sickness insurance contributions; the employer paid the other half. As from 1 July 2005, members of the statutory health insurance scheme also pay an income-linked contribution of 0.9% to which employers do not contribute. As from 1 July 2005, all statutory health insurance funds have reduced their contribution rates by 0.9 percentage points.
In 2007, a new top income tax rate of 45% was introduced for taxable income above EUR 250 000 (EUR 500 000 for jointly assessed spouses).
In 2009, the bottom income tax rate was reduced to 14%. The basic allowance was increased to EUR 7 834. All thresholds were increased by EUR 400.
Since 1 January 2010, the basic allowance has been augmented to EUR 8 004 and all thresholds have been increased by EUR 330. Furthermore, new legislation improves the tax treatment of expenditure on health insurance and long-term care insurance. As of 1 January 2013, the basic allowance rose to EUR 8 130. As of 1 January 2014, the basic allowance was increased to EUR 8 354. As of 1 January 2015, the basic allowance amounted to EUR 8 472. The standard relief for lone parents adds up to EUR 1 908. Lone parents are entitled to an extra allowance of EUR 240 for the second and each subsequent child. The standard tax allowance for lone parents will be raised temporarily from EUR 1 908 to EUR 4 008 in the years 2020 and 2021 in order to stabilise the income of single parents.
Since 1 January 2016, the basic allowance has been risen to EUR 8 652. As of 1 January 2017, the basic allowance was enhanced to EUR 8 820. Since 1 January 2018, the basic allowance has been augmented to EUR 9 000. As of 1 January 2019, the basic allowance was raised to EUR 9 168. In 2020, the basic allowance amounts to EUR 9 408.
4.1. Changes to labour taxation due to the covid-19 pandemic
In 2020, families with children will receive a one-time bonus benefit payment of EUR 300 per child. The bonus will not be offset against basic income support for jobseekers. However, in the case of households with higher incomes, the bonus will be offset against the tax allowance for children.
The standard tax allowance for lone parents will be raised temporarily from EUR 1 908 to EUR 4 008 in the years 2020 and 2021 in order to stabilise the income of single parents.
5.2. Employer’s contributions to private pension, etc. schemes
No information available, though such schemes do exist.
The equations for the German system in 2020 are mostly calculated on a family basis.
The standard functions which are used in the equations are described in the technical note about tax equations. The function acttax carries out a rounded calculation for the tables but the unrounded version purtax is used in calculating the marginal rates.
For a taxpayer with children, either the child allowance is given in the tax calculation or the cash transfer is given if this is more beneficial. In practice, therefore, it is necessary to make two calculations - with and without the child allowance. Nevertheless, the calculation of solidarity surcharge is always based on the calculation which does assume that the child tax allowance is given.
Variable names are defined in the table of parameters above, within the equations table, or are the standard variables “married” and “children”. The affixes “_princ” and “_spouse” on Variable names in functions indicate that the values have to be calculated for the principal and spouse, respectively. The parameter year in function SSC_Allowance is the year for which you calculate the Allowance.